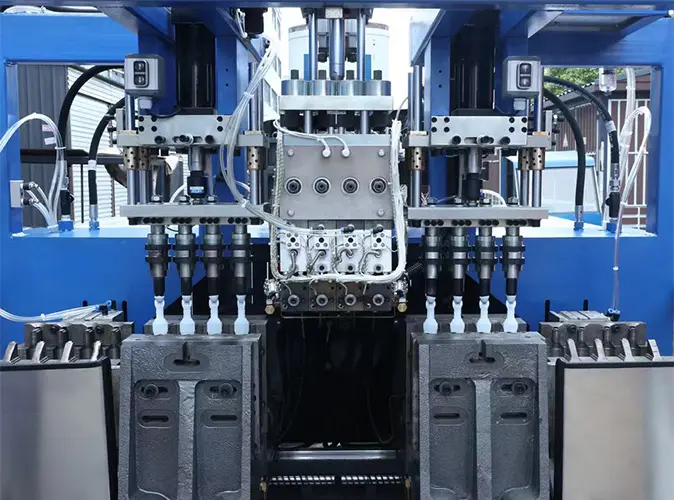
What is Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM)?
Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) is a manufacturing process used to produce hollow plastic parts, such as bottles, jerry cans, containers, and tanks. This technique involves melting plastic and forming it into a parison, which is then inflated inside a mold to take the shape of the desired product. EBM is widely applied in the packaging, chemical, automotive, and household product industries.
Key Steps in the Extrusion Blow Molding Process
- Plasticizing and Extrusion
The process begins by feeding raw plastic resin (typically HDPE, LDPE, PP, or PETG) into an extruder. The material is heated and mixed until it reaches a molten state. This melt is then pushed through a die head to form a hollow tube known as a “parison.”
- Parison Formation
The parison is extruded vertically and positioned between the two halves of a mold. The length and wall thickness of the parison are critical and can be controlled precisely through parison programming systems.
- Mold Clamping and Inflation
Once the parison reaches the desired length, the mold closes around it. Compressed air is blown into the parison, forcing the plastic to expand against the mold walls. This step shapes the product according to the internal geometry of the mold.
- Cooling and Ejection
The plastic part is cooled while still inside the mold, allowing it to solidify and maintain its shape. After adequate cooling, the mold opens, and the finished product is ejected. Trimming and leak testing are often conducted immediately afterward.
Machine Drive Types: Precision Meets Efficiency
– All Electric
All-electric machines are driven entirely by servo motors. They are ideal for clean environments such as food, pharma, and cosmetics due to their energy efficiency, low noise, and high precision.
– Servo Hydraulic
Combining servo control with hydraulic power, these machines offer a balance of strength and energy savings. Suitable for large and thick-walled containers, especially in industrial chemical or agrochemical applications.
Materials in Focus
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Best suited for robust, chemical-resistant containers.
- LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): Offers flexibility and softness, often used in squeezable bottles.
- PP (Polypropylene): Excellent clarity and heat resistance, commonly used in pharmaceutical and food-grade applications.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Good for transparent applications and impact resistance.
Application-Based Product Categorization
Food & Beverage
EBM containers for juices, dairy, edible oils, and sauces demand hygiene, consistency, and regulatory compliance—qualities well-matched with all-electric machines and food-safe HDPE or PP.
Daily Chemicals
Shampoo, detergent, and cosmetic bottles benefit from flexible design and high-volume output. LDPE and HDPE are commonly used depending on the desired rigidity.
Lubricating Oil
Durable, thick-walled HDPE containers are required to withstand oils and maintain shape integrity. Servo hydraulic machines are often preferred.
Pharmaceutical
Precision and cleanliness are crucial. All-electric machines with PP or HDPE material ensure pharmaceutical-grade compliance and clarity.
Agrochemical
Leak-proof and UV-resistant containers are produced using HDPE on servo hydraulic machines for strength and resistance to corrosive chemicals.
Chemical & Industrial
Large drums and jerry cans made from HDPE using servo hydraulic systems meet the demand for chemical durability and structural integrity.
Advantages of the EBM Process
- Cost-effective for medium to large production runs
- Capable of producing complex shapes and handleware
- Suitable for multi-layer and barrier packaging
- Easy integration with automation systems like trimming, leak testing, and labeling
Considerations for Machine Buyers
When selecting an extrusion blow molding machine, factors to consider include:
- Product size and geometry
- Required output and cycle time
- Material compatibility
- Level of automation
- Energy efficiency (servo vs. hydraulic systems)
Conclusion
Extrusion Blow Molding is more than just a manufacturing technique—it’s a versatile solution adaptable to industries with diverse packaging needs. Whether you require a high-precision pharmaceutical bottle or a rugged chemical drum, the combination of the right material, drive system, and machine configuration ensures optimal results.
At Youli, we design and export custom extrusion blow molding machines tailored to your specific application, material, and production volume. Feel free to contact us today to place your order!